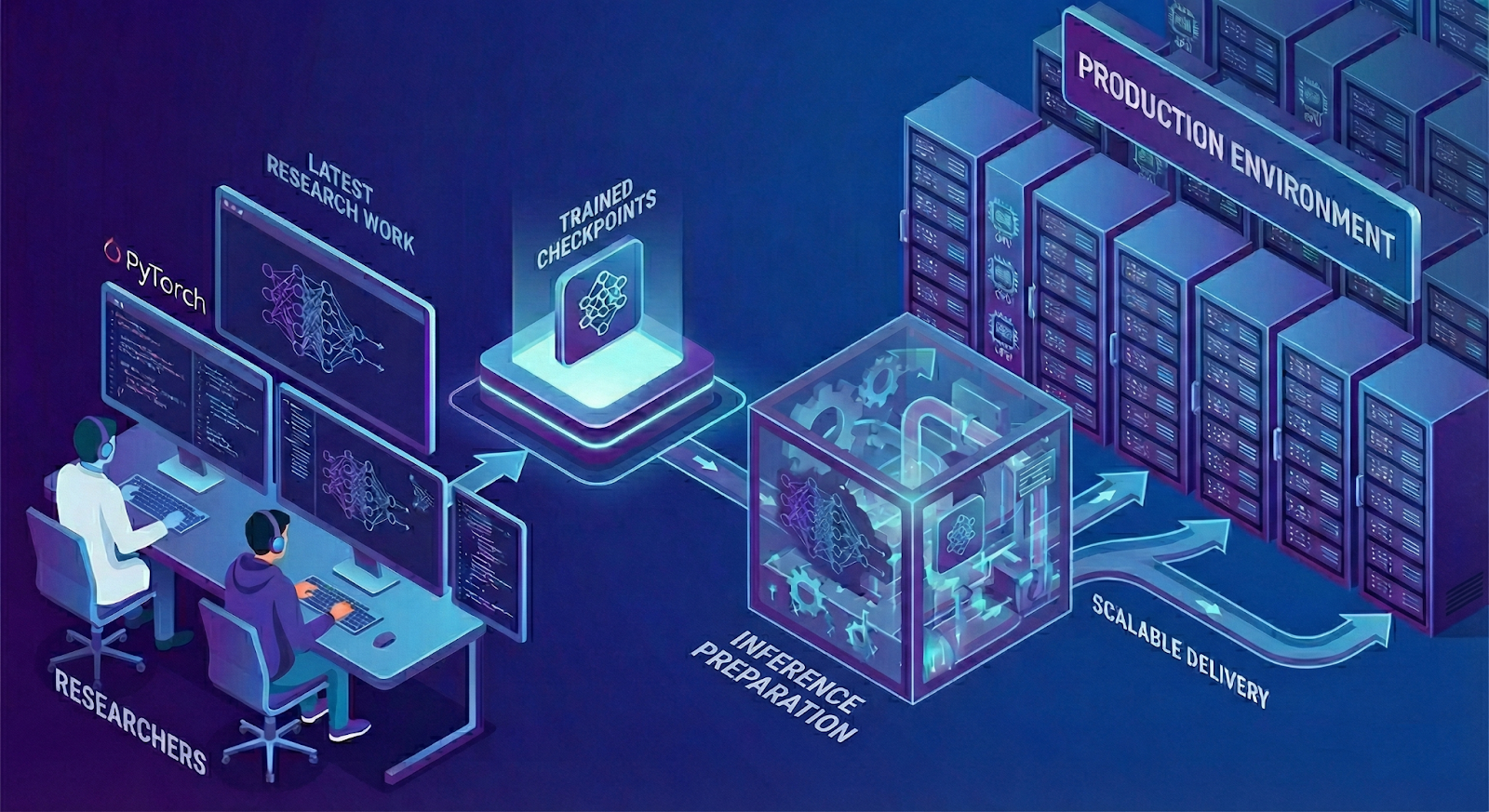
Meta has developed a PyTorch-based inference system for recommendations, designed to quickly translate research advances into real-world applications. This system supports diverse ML architectures, from DLRM model extensions to advanced techniques like DHEN and HSTU.
Overall Workflow
The system converts trained models into optimized inference models, ensuring efficient hardware utilization and high performance (QPS) with low latency. This process includes defining a dedicated inference model, capturing the computation graph, and applying transformations and optimizations.
Model Transformation and Optimization
Transformations include model splitting for distributed inference, operator fusion, quantization, and compilation. Model serialization uses formats like TorchScript and torch.export to ensure backward compatibility and resolve Python dependency issues.
Model Loading and Execution
After preparing the inference models, the runtime processes the requests. A PyTorch-based inference server manages serving, with a lightweight executor wrapper, flexible tensor-based APIs, and a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) representation of the model.
Key Optimizations
Optimizations include GPU inference, using a C++ runtime for high QPS, distributed inference (CPU-GPU, embedding-dense, dense parallelism), AI compilers (AOTInductor, AITemplate, TensorRT), and high-performance kernel libraries (CUTLASS, Composable Kernels, ZenDNN, OneDNN).
Other techniques include request coalescing, table batched embedding, quantization (bf16, int8, int4), and delta updates to maintain model freshness.
💬 Commenti (0)
🔒 Accedi o registrati per commentare gli articoli.
Nessun commento ancora. Sii il primo a commentare!